Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Wu, C.*; Tanaka, Kazuya; Tani, Yukinori*; Bi, X.*; Liu, J.*; Yu, Q.*
Science of the Total Environment, 821, p.153265_1 - 153265_9, 2022/05
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:94.35(Environmental Sciences)Microplastics (MPs) with different particle sizes were co-cultured with a model freshwater fungus, 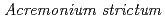 strain KR21-2, to form biofilms on their surface. We also determined the changes in surface physicochemical properties of the biofilm-covered MPs (BMPs) and the heavy metal adsorption capacity of the original MPs and BMPs. The results revealed that the biofilms improve the adsorption of heavy metals on MPs, and the particle size of MPs plays a crucial role in biofilm colonization and adsorption of heavy metals by BMPs.
strain KR21-2, to form biofilms on their surface. We also determined the changes in surface physicochemical properties of the biofilm-covered MPs (BMPs) and the heavy metal adsorption capacity of the original MPs and BMPs. The results revealed that the biofilms improve the adsorption of heavy metals on MPs, and the particle size of MPs plays a crucial role in biofilm colonization and adsorption of heavy metals by BMPs.
Amano, Yuki; Iwatsuki, Teruki; Naganuma, Takeshi*
Geomicrobiology Journal, 34(9), p.769 - 783, 2017/03
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:21.84(Environmental Sciences)Two biofilm samples were collected from anaerobic groundwater in a borehole drilled in the Tono area, Japan, to understand the effects of biofilms on the migration behavior of heavy metals in subsurface environments. Biofilms grown on in groundwater of sedimentary rocks and granite groundwater were characterized geochemically and microbiologically, and their heavy metal sorption capability was examined. Clone library analysis was constructed from the biofilms to evaluate microbial community composition. From the results of 16S rRNA gene analyses using clone libraries, it was found that these microbial community compositions in the biofilms were clearly different from the composition of unattached, planktonic microorganisms in the groundwater samples. Furthermore, the microbial community structures generated in each biofilm were different, depending on the groundwater type. It is shown that the community structure of biofilms lacked diversity in groundwater types obtained from sedimentary and granitic rocks. These results indicate that biofilms are formed in natural subsurface environments with site-specific community compositions. High amounts of heavy metals such as Fe, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, Pb, Th, and U accumulated in the biofilms, and their sorption properties varied in each elements. These results provide important insight on heavy metal sorption capability by biofilms.
Amano, Yuki; Beppu, Hikari*; Sato, Tomofumi*; Mochizuki, Akihito; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
no journal, ,